Angel Theory’s M-Systems
Chapter 2: The Theory of Everything
By Nick Ray Ball 29th August 2017

In physics ‘The Theory of Everything’ (M-Theory) is what can unite the subatomic world and Einstein’s Theory of Gravity. It describes the forces of nature and the fabric of the universe. But can M-Theory also be used in economics?

Welcome to Angel Theory Chapter 2: ‘The Theory of Everything.’ Following the excitement of the Angel City 5 chapter told via the power of film, this chapter fully describes the so called ‘quantum data’ and aims to teach and ‘blow the minds’ of attentive readers who do not know the theory of everything (M-Theory) by associating the components of it with everyday experiences; and ‘blow the minds’ of the world’s elite theoretical physicists seen within by presenting it as a tool for modelling economics, which can provide testable results. In addition, this chapter provides a practical explanation of the POP Investment System for companies that wish to join the network.
In physics, ‘The Theory of Everything’ is what can unite quantum mechanics (the subatomic world) and Einstein’s Theory of General Relativity (gravity, space, and time).
For the last 49 years, physicists have attempted to unravel this mystery with String and M-Theory.
This chapter was inspired by ‘The Network on a String’ http://americanbutterfly.org/pt3/the-network-on-a-string (circa November 2012).

In 2012 ‘The Network on a String’ was the 3rd instalment of ‘American Butterfly’ that added elements of string theory and supersymmetry to the previous chaos and quantum theory influenced instalments. ‘The Network on a String’ presented 8 ways that the original http://AmericanButterfly.org book; ‘The Theory of Every Business,’ could be improved by considering simulated behaviours mimicked from TOE (Theory of Everything) physics.
String Theory is the idea in physics that every sub atomic particle is created by a tiny vibrating string and that the universe is its orchestra, a very compelling vision.

“Ever since Newton and especially since Einstein, the goal of physics has been to find a unified Theory of Everything.
M-Theory is the only candidate for a complete theory of the universe.
M-Theory is the unified theory Einstein was hoping to find.”
By Professor Stephen Hawking

One problem with string theory is that the ‘strings’ are so small we just can’t see them. In terms of scale, in comparison to the size of string, each of us are almost the size of an entire universe. And because of this in physics, despite string theory’s 49 years of intense and exhaustive study, it is experimentally unproven.
However, as a branch of pure mathematics, it is without doubt the most fiendishly clever and economical mathematics ever created, as when you work in string or M-theory you are effectively working in both quantum mechanics, special and general relativity at the same time.

As Einstein once said, ‘Pure mathematics is the poetry of logical ideas.’ And whilst pure mathematicians often pride themselves at being the most impractical of all scientists; where the more abstract and useless the mathematics, the better. Often, pure mathematics finds its way to a practice purpose in the end.’
By Professor Michio Kaku (Paraphrased)
In this book, ‘Angel Theory’ suggests that chaos theory, quantum mechanics, relativity, string theory, and M-theory can be simulated and applied to business science and economics; and that M-Systems is a good M-theory influenced economic framework.
For a long time, the question: ‘Can we consider M-Theory as an economic science?’ has attached itself to Angel Theory’s M-Systems.’ Indeed, it has become its slogan.
“M-Theory an economic science?”
First written on the graphic below for the father of M-Theory, Professor Ed Witten.

“I feel that we are so close with string theory that – in my moments of greatest optimism – I imagine that any day, the final form of the theory might drop out of the sky and land in someone’s lap.”
Professor Edward Witten
Father of M-Theory, Winner of the Fields Medal
Charles Simonyi Professor at Princeton University
To Professor Witten and colleagues, we say, “Of course, this is not the final form of the theory, but is it a form of the theory?”

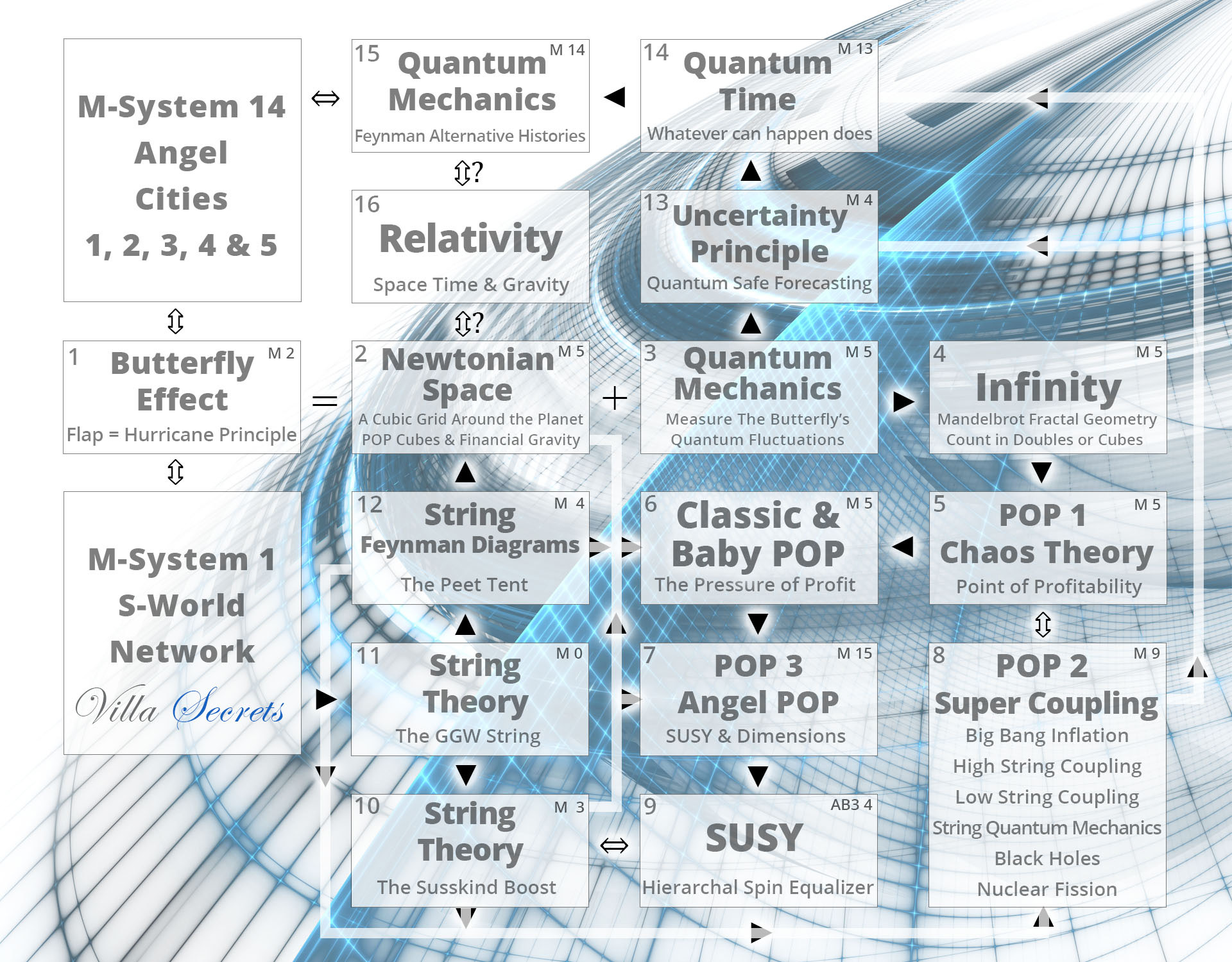
Below we see the latest system architecture (The ‘quantum data’ sent back in time to create S-World UCS in Chapter 1 for the Angel City 5 movie framework).
M-Systems POP System Architecture
(Note we do not strictly follow the order of the steps below during this presentation)
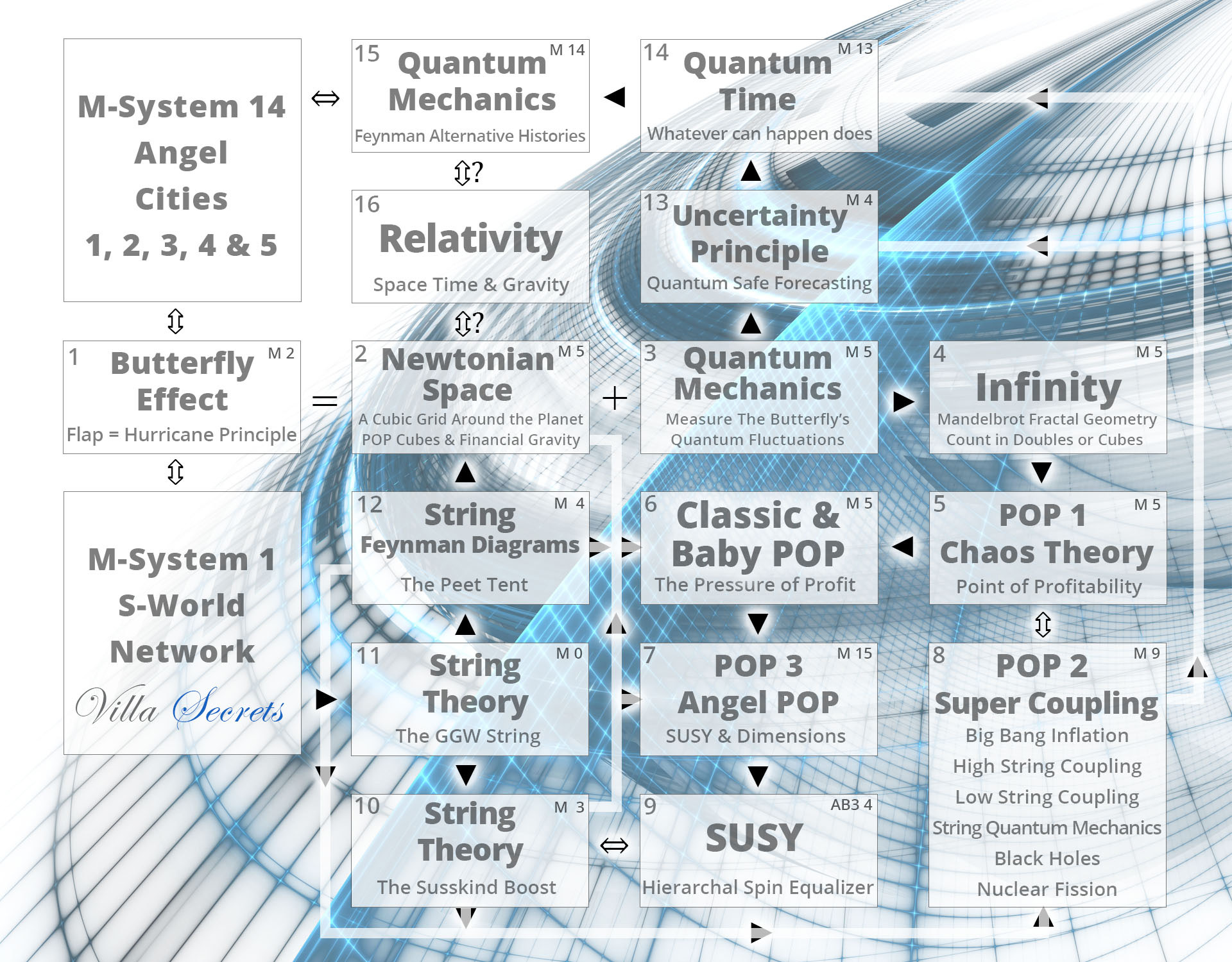
M-Systems an Economic Theory of Everything
Before we continue, please note this chapter is not the correct place to judge the effectiveness of M-System 1. S-World Villa Secrets, which is its own microeconomic miracle. For fuller description, see network.villasecrets.com. For now, please trust that the forecasting scenarios for Villa Secrets are well constructed.
POP – Microeconomics & Villa Secrets
POP works in discrete quanta, this means there are only certain figures we can use, multiples of $0.01 cents x 8 repeatedly… $0.01 x 8 = $0.08 x 8 = $0.64 x 8 = $5.12 x 8 = $40.96 x 8 = (D1) $327.68 x 8 = (D2) $2,621.44 x 8 = (D3) $20,971.52 x 8 = (D4) $167,772.16 x 8 = (D5) $1,342,177.28 and so on.
The (D) that you see is the financial cubic dimension. The objective is to collate a set of companies’ POP points (discussed soon, for now just think in terms of profit made in a year) into higher dimensional cubes. So, for instance in the 5th cubic dimension of (D5) $1,342,177.28 can be made up of 8 different companies of different multiples of (D3) $2,621.44; some may be 8 times (D3), some 6 and some 10, just so long as the (1st tear) network adds up to (D5) $1,342,177.28.

In our current testing location of Cape Town, we are creating a (D5) primary network, where after from 25 or so different related industry niches we intend to increase the network to over 100 separate companies equalling (D6) $10,737,418.24. Which we must half as 50% of profit returns to stakeholders and 50% becomes POP investment capital. So, creating $5,368,709.12 in POP Investment.
It’s important to note that companies only pay POP when they make a specific target; and in the case of Cape Town this target is when the business creates a 400% return on investment per year, relative to its initial investment (that’s 400 times what one would get from a Western bank, plus of course the time of the stakeholders.)
In California state, we would be disappointed not to reach (D7) and generate POP investment of $42,949,672.96 by 2021 (or sooner if partnerships are made with the Chan Zuckerberg, Paul G Allen and other technology-based foundations).

This project is told in great detail on http://network.villasecrets.com, since 2013 and the completion of American Butterfly, Villa Secrets and the microeconomic network has been written in much greater detail than Angel Theory. As without the microeconomics there is no macroeconomics to calculate; and equally important, the 20 unique and beneficial systems and software components are the foundation for the success of every S-World company.
However, Angel Theory Part 2. ‘The Theory of Everything’ deals with the macroeconomics and the creation of grand and super grand networks. A grand network is a resort styled real estate development that needs to produce $85,899,345.92 in POP investment, initially created in an area of abject poverty, which is twinned (has symmetry) with a virtual (no resort development) network such as S-World Villa Secrets California, and another prime territory such as ‘Florida.’
Angel POP – A Philanthropic Theory of Everything

Angel POP creates symmetries between prime investment opportunities and opportunities that would be considered economically unviable (an abject network). And it restricts the growth of the network so that for every prime network created, there must also be an abject network.

“Grand Networks in areas of Abject Poverty are Special Projects’
As POP investment goes towards the creation of grand networks, which in turn create the (Angel City 5) philanthropic, social, scientific and ecological special projects.
Everyone that invests, owns, works for, or buys from an S-World company is contributing to the special projects, every day, and every purchase.
Next, we see the most recent system architecture for POP interactions within M-Systems.
POP was the original idea in 2011 that sparked American Butterfly and since S-World Villa Secrets and Angel Theory’s M-Systems.
POP – An Economic Theory of Everything (E-TOE)
Steps 1-3. POP Origins (The Butterfly Effect)

The Butterfly Effect, Newtonian Space, and Measuring at a Quantum Scale
In and around the Autumn of 2011, starting with limited knowledge of pure math, zero knowledge of theoretical physics (and certainly no idea about Einstein’s theory of special relativity); the initial journey to the discovery of POP was a consideration of ‘the butterfly effect’ and the saying:
“Can the flap of a butterfly’s wing in Brazil create a tornado in Texas?”

To create a solution, I conducted a thought experiment and pictured an imaginary cubic grid around our earth in every direction.
And inside one cube was our butterfly; where after using a future technology, one could measure the tiny disturbances in the ‘breeze force’ created by the flap of the butterfly’s wings and then calculate across all cubes to see if that flap did or did not cause the tornado?

About a year later, courtesy of Professor Brian Green’s’ ‘The Fabric of the Cosmos’ and ‘The Elegant Universe,’ this grid was seen to be common with Sir Isaac Newton’s picture of gravity and Einstein’s theory of special relativity (Michofski space-time). And the idea of measuring the tiny disturbances was not unlike quantum mechanics, so making this little idea not unlike ‘a theory of everything.’ Just add Einstein’s theory of gravity and all the components are there.

This is important as it helps to explain the methodology of how one goes from a theory in physics to a theory in business and economics. Put simply, whenever a part of the network design is seen to be similar to a system that describes nature, we pay a lot more attention to it, and we look at all sorts of TOE physics to see if we can find inspirations; and over the years, these symmetries and simulations have built up and fit together magically.
In Professor Stephen Hawking & Leonard Mlodinow’s book ‘The Grand Design,’ a very simple and solid thread for why following the laws of nature, as described by M-theory, would be an advantage in economics is presented.

“The laws of nature are meant to economically compress a number of particular cases into one simple formula.”
When designing a system for oneself, one has infinite amount of options. And each is its own theory, which may or may not work out the way one planned. By following the laws of nature, one not only has a road map of sorts, one is benefiting from billions of years of fine-tuning. And due to that fine-tuning the components in the system are economically compressed. So, all parts of the system work well together, even if there was no strict plan for such by the designer.
However, we all have to start somewhere. And in the case of Angel Theory, certainly in terms of ‘theory of everything’ related systems, the beginning of this journey was the original thought experiment of the butterfly within the cubic grid; and with this consideration on my mind, I looked at the parent discipline of the butterfly effect, ‘chaos theory.’
Chaos Theory (2011)

The next consideration was the chaos theory riddle of rounding errors, created by rounding numbers in general and infinite numbers like 3.33333 recurring.
Because of the butterfly effect; even the smallest of inconsistencies could spiral into a tornado and was enough to rule out any kind of long-term forecasting in any complex systems such as the weather or our economy.
Step 4. The Mandelbrot Set (2011)

To solve this, I looked at the problem from a different direction. And after some research, including the Mandelbrot Set Fractal that beautifully recreates itself in an infinite pattern, I had the idea for ‘compatible finite mathematics’ that flew in the slipstream of infinity.
For the original inspiration, see www.S-World.biz/TST/EEE-14Billion_Years.htm (Nov 2011).
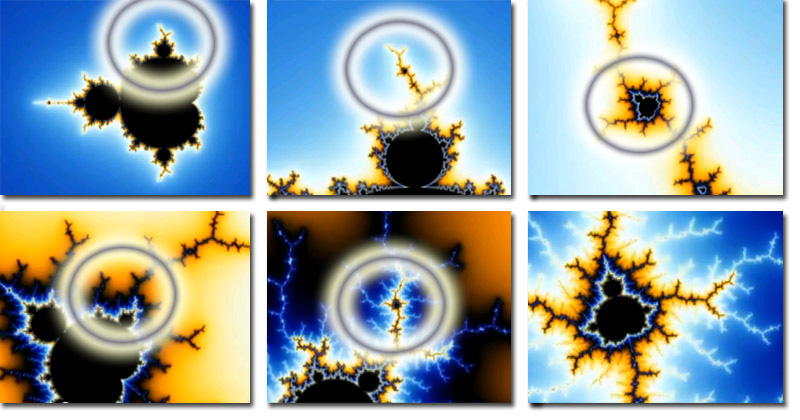
A simple solution was to count and create a framework with numbers that doubled, as that makes recurring numbers harder to create. So, 2 > 4 > 8 > 16 > 32 etc.
However, considering the cubed grid around the world, this soon turned into multiplying by 8. So, 1 > 8 > 64 > 512 > 4,096 > 32,768 as multiplying by 8 creates cubes inside of cubes.
Step 5 – (M-System 5) The POP; Point of Profitability – POP Cubes (2011)
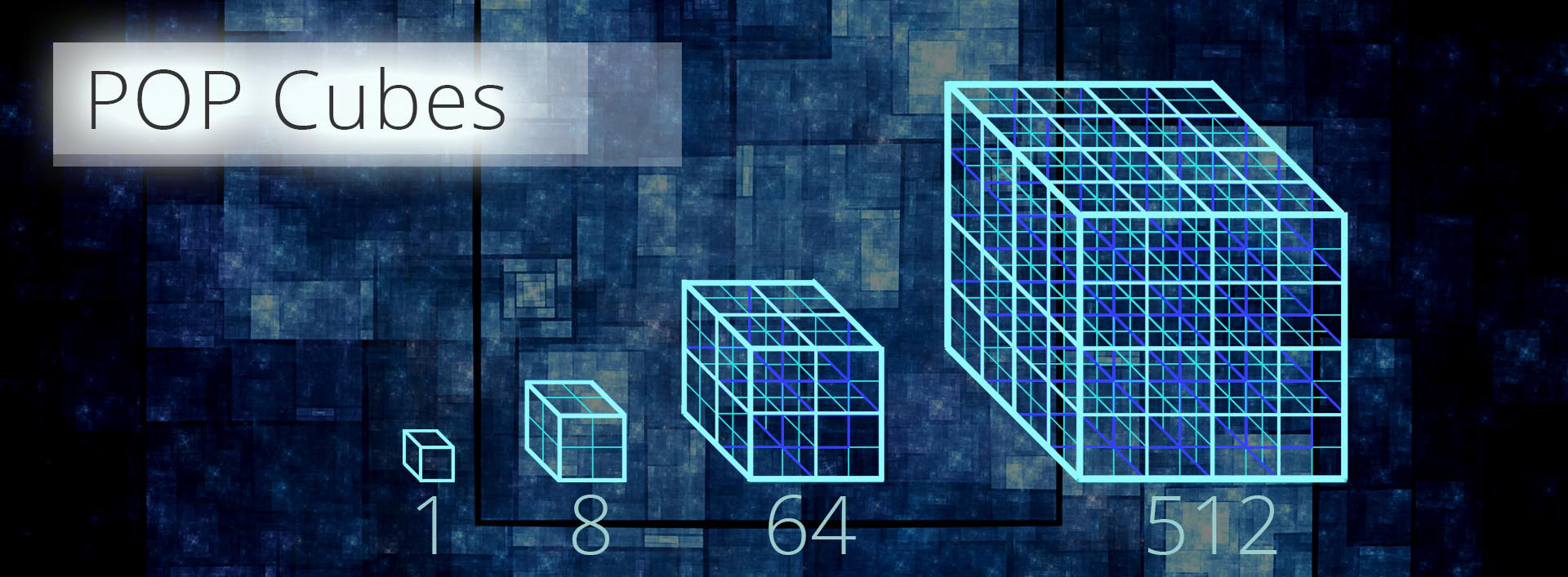
If we create a point of profitability, where after all profit overflows into creating a new company or network, then by working in multiples of 8, we create predictable cubes of underlying profit that have no errors to round.
Once a cube is full and each company within has achieved its POP point, the cube would represent a single block of underlying profitability, and could be counted simply as 1. And other cubes created counted as 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 at which point we created a larger dimensional cube, representing 8 networks of companies making their POP points. This follows to the next dimension of 64 and then next at 512 companies all making their POP points.

By working in this way, we create an underlying stable economic framework that is not affected by rounding errors as there are no recurring numbers to round. One simply counts the full POP cubes.
Which as Sir Isaac Newton’s theory of gravity is often presented as the universe within a cubed framework eventually took on the name ‘financial gravity.’
Of course one needs to maintain the integrity of each company within each cube, and that’s where POP meets string theory and ‘The Susskind Boost’ & ‘The Peet Tent,’ which we address shortly.
Step 6 (M-System 5) – The POP Investment Principle – The POP Train (2011)
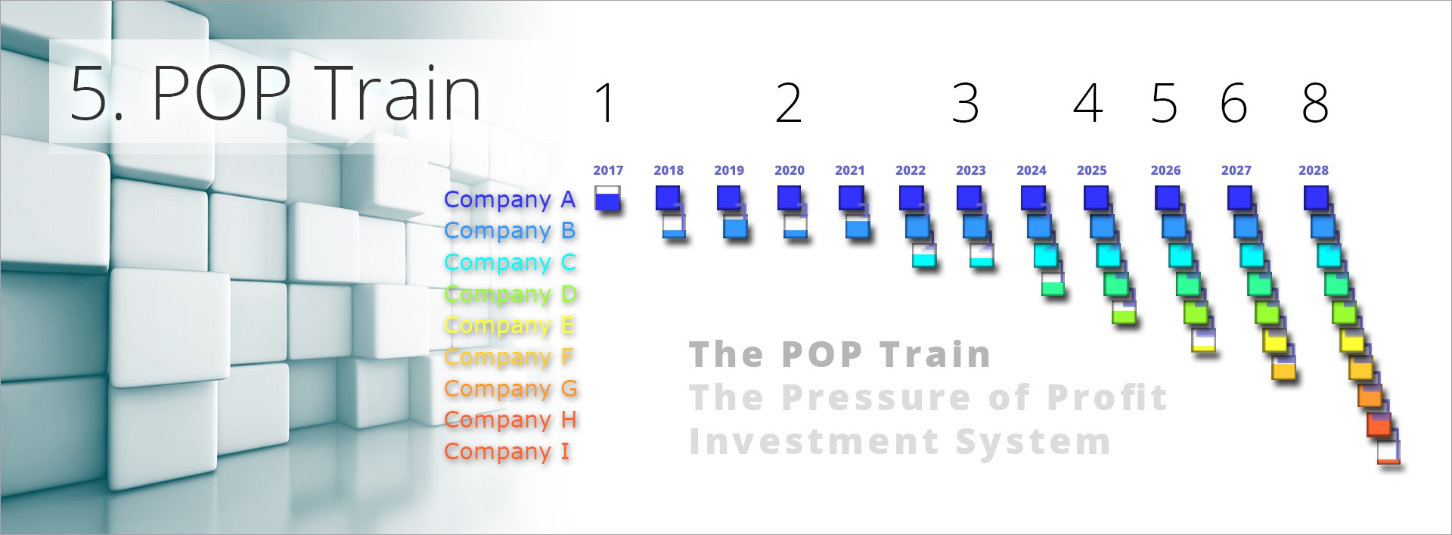
What turned a mathematical curiosity into the mathematics that underpinned the entire project was revealed when making the graphic you see above, called the POP Train.

This point may have been subconsciously influenced by the South African Bulls rugby team and their train tactic; where three, then four, then five players line up behind the ball carrier and push in series, and the pressure of 5 teammates pushing in a line breaks through the opposing team’s defence.

When investing in a POP train, all the POP investment from the first network of companies flows into the second (and we call the object that the overflow falls into a ‘bucket’). Once bucket 2 is full, both networks 1 and 2 combine to fill ‘bucket 3.’ And once bucket 3 is full, networks 1, 2, & 3 combine to fill ‘bucket 4.’ After which new networks are created annually and the network snowballs and grows exponentially, as we see after the 11th year more than 2 new buckets are created within a year.

Hence POP ‘The Pressure of Profit,’ as the more companies in the train, the greater the pressure and the faster new networks are created.
“It’s a bit like pushing a bus over a cliff edge, it takes some effort to get it started, but when it goes, there is no stopping it.”
Quote by Brian Cox and Jeff Forshaw
Please note this version of POP is for grand networks (large resort developments). If we were to look at the POP of an individual company, it could create more than 2 new companies a year by its 3rd year.
Also note that when a company reaches its POP point and exactly half of its shareholders profit is being invested in POP opportunities, then from that moment on all additional profit is shared; half for stakeholders, half to more POP opportunities and special project commitments.

Of course, in a system of thousands of cubes, each containing thousands of individuals and companies, where we count the cubes in sets of 64; often there may be a few inner dimensional cubes that have fallen out of POP (had made it to their POP point but since slid backwards). So, we must count 61 of 64, 57 of 64, 63 of 64 and so on.
This can create rounding errors and that’s why in 2012 we called it, ‘compatible finite math,’ as the math is not perfect, just better. However, when we added string theory to maintain and repair the POP cubes that had fallen backwards we can bring all networks back to 64/64.
String theory is important to the economics as it maintains the integrity of our cubic economy and is necessary in theoretical physics to do much the same; but for the fabric of our universe at extreme points such as black holes and the big bang, where there is a lot of heavy stuff, but it’s all very small (quantum gravity).
To help fill in the gaps and fuel networks that have fallen behind (were making POP investment but are no longer), we need to move into string theory and skip forward to step 10: M-System 3. The Susskind Boost.
Step 10. (M-System 3). The Susskind Boost (April 2016)
Source: Leonard Susskind-Lecture 1 | String Theory and M-Theory
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=25haxRuZQUk

‘We boost the hell out of the system along the Z axis (gross profit) until every single particle (company) has a huge momentum.
If there is any particle (company) that is going backwards along the Z axis (gross profit), you just have not boosted it enough.
Just boost it some more until it’s going forward with a large momentum.’
To apply this to the network, we change a particle for a company and the Z axis to gross profit. And in general, we always boost the weakest companies in the network until they are going forward and are creating a healthy POP investment.

There are tonnes of ways to boost a company’s profit without giving direct financial assistance.
Here are some options: Ť the award of tenders, Ŵ additional websites, Ƈ = contracts or mandates, higher ROI advertising, or making a company’s goods or services a preferred purchase for those who have network credits (Planck Cubits).

However, if a company is in actual trouble, we apply ‘The Peet Tent,’ the shape of the GGW String that assists troubled companies, giving them the lift to be further boosted by The Susskind Boost; which will continue to boost the companies until they are creating POP again, so repairing the integrity of each network’s cube until we see 64/64 across the board. This process never ends, but will become mostly unnecessary for established cubes when the network becomes massive.
Step 11 (M-System 0) – The GGW String (Greene/Green/Witten) (Late 2016)

Named after the 3 physicists: Brian Greene, Michael Green & Edward Witten, who from 2012 to 2016 assisted our basic understanding of string theory.

The GGW string considers the most fundamental properties of string theory; ‘the strings themselves’ and that a good simulation in economics is for strings to be equivalent to the money earned by the S-World Network (the holding company/foundation/operating system), and the different ways we spend the money are the different shapes of the strings.
Instead of POP investment, the GGW String primarily receives its income from the gross profit from each company within the network.
However, after reading ‘The Real Crash’ by Peter Schiff, a solid case was made for lowering or removing direct taxes on company’s income. Remember POP only applies after a company has done very well, and even then, it’s an investment not a tax. But the GGW-String income is a direct tax on profits.
One can say that such a direct tax on gross profit is the equivalent to a standard franchise fee. However, in creating M-System 1. Villa Secrets, it was decided that the 5% equivalent of a franchise fee should be lowered closer to 2.5%, at least until the bulk of the systems were developed. And that the 2.5% be used almost exclusively for web, software, and network development; creating the systems that directly increased profit for the networks thus creating a Nash Equilibrium.

Professor John Nash, winner of 2 Nobel Prizes and famous for being the subject of the Oscar winning film ‘A Beautiful Mind.’
A Nash Equilibrium is most often seen within game theory, it is in essence a win/win scenario, where one would choose the same outcome regardless of enforcement.
In the case of S-World Villa Secrets and the 2.5% of turnover contribution towards the development of software and the network, this is forecast to return from 25% to over 100%. So, to make a 25% or more increase from a 2.5% contribution is an action any sane company or individual would choose to make; hence a Nash Equilibrium, of sorts.
However, it is quite possible that at a later point this percentage will increase to provide some GGW String funding, which may be fully exclusive to the Susskind Boost and Peet Tent and seen as an insurance contribution, insuring the integrity of the network and every business within.
Step 12 (M-System 4) – The Peet Tent (Nov 2012 to 2017)

The Peet Tent was the principle of physics from American Butterfly in 2012 that became the foundation for Angel Theory’s M-Systems in March 2016.
But first a little history. Before starting S-World in 2011 between 2008 and 2011 while researching the Virgin network, it was noted that Sir Richard Branson made mention that the Virgin Network is a network of different companies (as is S-World). But in the case of Virgin (and most such groups), if one company failed, it was detached from all others, so all others were safe. This is of course the sensible way to create a network and was respected, but it was not in the spirit of ‘A Theory of Every Business.’
The Peet Tent is the answer to this dilemma.
Sources:
1. Dr Amanda Peet: String Theory for the Scientifically Curious
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PpQngpaHamg
2. American Butterfly Book 3 ‘The Network on a String’
http://americanbutterfly.org/pt3/the-network-on-a-string/cfm-pop-analogies
3. Dr Amanda Peet: String Theory Legos for Black Holes
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MlDd2HtFfPU
The Peet Tent is a shape of the S-World string that protects companies from failure within the network.
Below on the right we see what is known as a ‘String Feynman Diagram’ (also known as a baggy pants diagram) adapted to M-Systems, where instead of partials we see positive and negative financial results within the boundary of the pants/tent.

In string theory this is it, the theory of everything; as this is how the jittery and unpredictable results from quantum mechanics unify with the smooth results from general relativity (Einstein’s theory of gravity) as they all fit within the string theory Feynman diagrams baggy tent. This is also why string theory is said to be a very economic theory.
In the end, the simulation in economics was simple enough, (albeit it would take years to work out) one must make provision for companies in trouble. If applying the Susskind Boost did not work by adjusting opportunities, one must apply The Peet Tent; which provides direct income to the Susskind Boost, so boosting troubled companies back to health and then fitness.
This works equally for companies on their way to POP and for companies that have achieved POP but have fallen backwards.
So long as there was enough income in the GGW String, all companies are safe, permanently.
Professor Edward Witten, Standard and String Feynman Diagrams
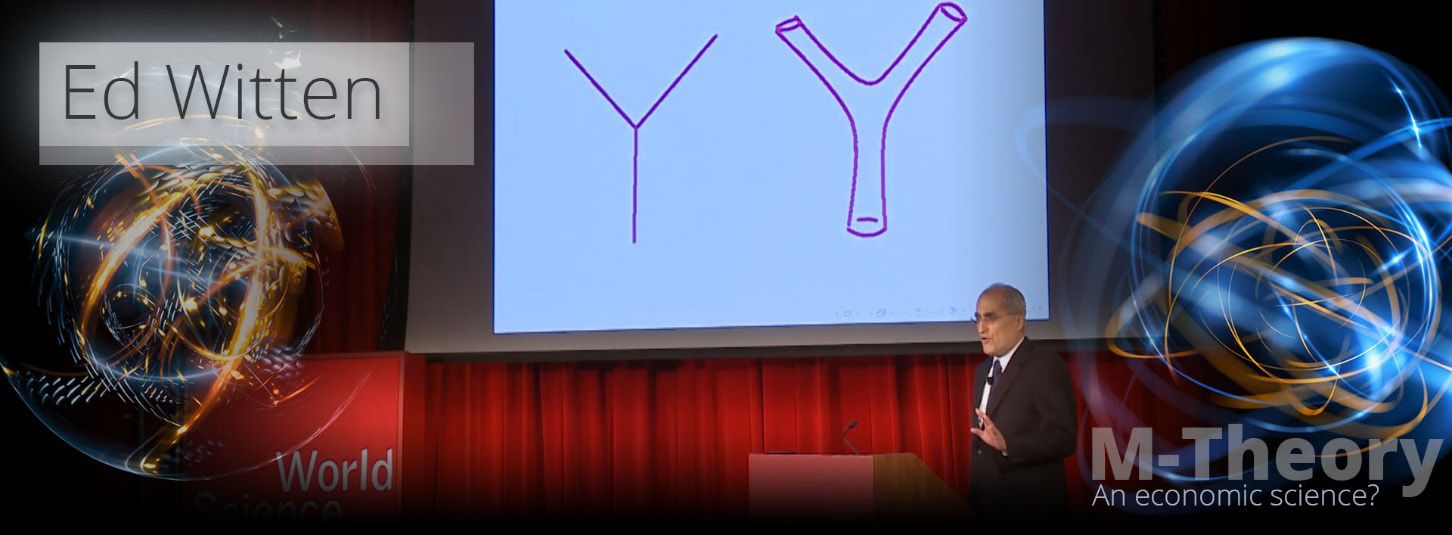
Above we see Professor Edward Witten present both the standard Feynman diagram in quantum mechanics and the string version; and as you can see in the standard quantum version, there is no tent at all, hence only by using string theory can the physics be unified, so creating a TOE.
The Peet Tent Limited Liabilities
For now, before the system is massive, there are some practical limitations such as provisions against lawsuits that would not have been made if not for the deep pockets of The GGW String, and the many systems of M-System 1 and especially S-World TFS™ (Total Financial System) and S-World CRM CC™ (Company Controller); which collectively keeps a careful watch of every penny made and spent by every company, so we can see problems before they occur, which can mostly be fixed via better management and The Susskind Boost.

And in addition, comes step 13. QSF (Quantum Safe Forecasting) which we shall look at shortly.
Before we carry on let’s see the system architecture again.
So far, we have looked at the original chaos theory inspired POP steps 1 to 6, plus the string theory steps 10 to 12; which creates the network’s underlying financial gravity and maintains its integrity. Next, we move onto step 6b ‘Baby POP’ and see the creation of a cube of grand networks and ‘the boat.’
Step 6b (M-System 5) – Baby POP – Grand Networks POP Train & Boat (2012)

Baby POP was a derivative of the original POP investment principle for super grand networks that required a large investment and POP point for an initial super-grand network, but smaller investments and POP points for its offspring.
Like Classic POP, Baby POP invests per the train method; in fact, Baby POP is the same as Classic POP, just the POP point for new grand networks created is lower. This story is told in detail as the introduction to American Butterfly Book 3: The Network on a String:
http://americanbutterfly.org/pt3/the-network-on-a-string/prequal-CFM-and-POP.










